276-386-6162
Dental Trauma: Understanding and Treating Injuries to Teeth and Oral Tissues
April 11, 2024
Emergency Dentistry
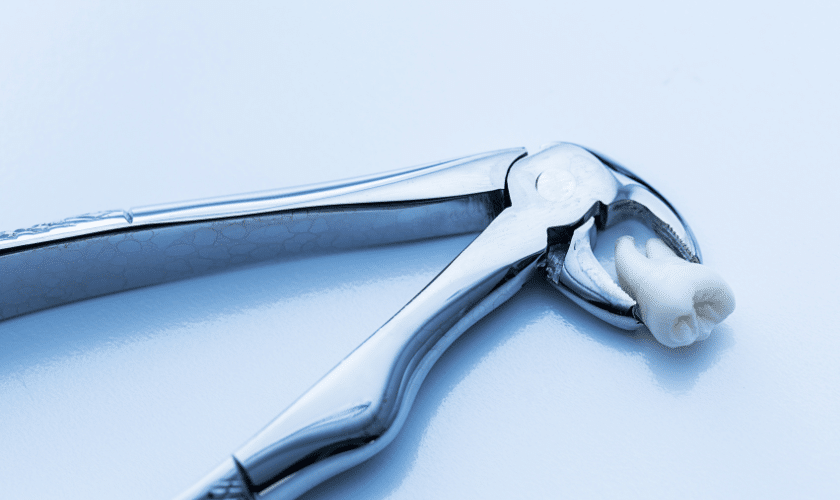

Dental trauma refers to injuries that affect the teeth, gums, jawbone, and other oral tissues, often resulting from accidents, falls, sports injuries, or physical trauma. Understanding the types of dental trauma and knowing how to respond promptly can significantly impact the outcome and long-term oral health. In this blog, we’ll explore dental trauma in detail, including its causes, types, symptoms, and treatment options.
Types of Dental Trauma:
- Fractured or Chipped Teeth: Commonly caused by falls, accidents, or biting on hard objects, leading to visible cracks, chips, or fractures in tooth structure.
- Avulsed (Knocked-Out) Teeth: Occurs when a tooth is completely displaced from its socket due to impact or trauma, requiring immediate attention to save the tooth.
- Luxated (Dislodged) Teeth: Teeth that are partially pushed out of their sockets, causing misalignment and potential damage to surrounding tissues.
- Soft Tissue Injuries: Trauma to the lips, cheeks, gums, or tongue, resulting in cuts, lacerations, or puncture wounds.
Symptoms of Dental Trauma:
- Pain or discomfort in the affected tooth or area
- Swelling, bruising, or bleeding in the mouth
- Visible cracks, chips, or fractures in teeth
- Loose or misaligned teeth
- Difficulty chewing or biting
- Sensitivity to hot, cold, or pressure
Treatment Options for Dental Trauma:
- Fractured or Chipped Teeth:
- Dental Bonding: Using tooth-colored composite resin to repair minor chips or fractures.
- Dental Crowns: Restoring extensively damaged teeth with customized porcelain or ceramic crowns.
- Avulsed (Knocked-Out) Teeth:
- Tooth Re-Implantation: Attempting to reposition and stabilize the knocked-out tooth in its socket.
- Tooth Preservation: Storing the avulsed tooth in milk or a tooth preservation solution until professional treatment is available.
- Luxated (Dislodged) Teeth:
- Dental Splinting: Securing the dislodged tooth in its proper position using a dental splint.
- Root Canal Therapy: Treating any damaged nerve tissue inside the tooth to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Soft Tissue Injuries:
- Wound Cleaning and Closure: Thoroughly cleaning and suturing any soft tissue wounds to promote healing and prevent infection.
- Antibiotics or Pain Medication: Prescribing medications to manage pain and prevent bacterial infections.
Prevention Tips for Dental Trauma:
- Wear protective mouthguards during sports activities or high-risk activities.
- Avoid chewing on hard objects like ice, pencils, or hard candies.
- Practice safe driving habits and use seat belts to prevent facial injuries during accidents.
- Schedule regular dental check-ups for early detection and management of potential dental issues.
Conclusion:
Dental trauma can range from minor injuries to severe damage, requiring prompt and appropriate treatment to preserve oral health and function. Understanding the types of dental trauma, recognizing symptoms, and seeking professional dental care without delay are crucial steps in managing dental injuries effectively. If you or a loved one experiences dental trauma, contact your dentist immediately for evaluation, diagnosis, and treatment tailored to your specific needs.
Recent Post

Aging Gracefully: Dental Care Tips for Seniors

Honoring Mom’s Smile: Personalized Dental Care Offers at Jeff Montgomery DDS for Mother’s Day
Dental Care for Children: Tips for Parents
Integrating Cosmetic Dentistry into Regular Dental Care: A Comprehensive Approach

